C programming – History
C Programming language টি 1972 সালে Denis Ritchie এবং K.N Thompson মিলে তৈরি করেন। তাঁরা এটিকে তৈরি করেছিলেন ইউনিক্স অপারেটিং সিস্টেমের(Unix Operating System) জন্য। C language একটি Procedural Programming Language যা structured, Moduler এবং Flexible হওয়ার কারণে অনেক জনপ্রিয়। এটি খুব দ্রুত কম্পাইল হয় এবং হার্ডওয়্যার প্রোগ্রামিং-এ ব্যবহৃত হয়। C programming language ডাটা স্ট্রাকচার(Data structure), ফাংশন(Function), পয়েন্টার(Pointer) ইত্যাদির মত বৈশিষ্ট্যগুলো রয়েছে। আজকের সময়ে এটি অনেক অ্যাপ্লিকেশন(Application), অপারেটিং সিস্টেম(Operating System), ইম্বেডেড সিস্টেম(Embeded System এবং গেম ডেভেলপমেন্টে(Game Development) ব্যবহৃত হয়।
What is Identifier in C and rule of writting Identifier ?
C Identifier: C Programming এ আইডেন্টিফায়ার (Identifier) হলো কোন ভেরিয়েবল(Variable), ফাংশন(Function), অ্যারে(Array), ইত্যাদির নাম। এগুলো প্রোগ্রামে বিভিন্ন উপাদানকে চিহ্নিত করে।
আইডেন্টিফায়ার(Identifier) লেখার নিয়ম:
- আইডেন্টিফায়ারটি অবশ্যই অক্ষর বা আন্ডারস্কোর (_) দিয়ে শুরু হতে হবে। সংখ্যা দিয়ে শুরু করা যাবে না।
- এর মধ্যে অক্ষর, সংখ্যা এবং আন্ডারস্কোর ব্যবহার করা যাবে। তবে স্পেস ব্যবহার করা যাবে না।
- C কিওয়ার্ড (if, else, while ইত্যাদি) আইডেন্টিফায়ার হিসেবে ব্যবহার করা যাবে না।
- আইডেন্টিফায়ারটি case sensitive। ‘age’ এবং ‘Age’ দুটি আলাদা আইডেন্টিফায়ার।
- আইডেন্টিফায়ারটি যতটা সম্ভব অর্থপূর্ণ হওয়া উচিত।
What is Literals in C programming ?
C Programming Literals : লিটারেলস (literals) হলো এমন কন্স্ট্যান্ট ভ্যালু(Constant value) যা প্রোগ্রামের মধ্যে সরাসরি লেখা হয়। একটি লিটারেল( literal) হলো একটি ডাটা এলিমেন্টের ভ্যালু (Data Element value)। C programming এ পাঁচ ধরনের লিটারেলস(literals) রয়েছে:
- ইন্টিজার লিটারেলস(Integer Literals): C তে ইন্টিজার(Integer) ডাটা টাইপের জন্য ইন্টিজার লিটারেলস(Interger literals) ব্যবহৃত হয়, যেমন: 10, 200, etc
- ফ্লোটিং পয়েন্ট লিটারেলস(Floating Literals): ফ্লোটিং পয়েন্ট (Floating point) ডাটা টাইপের জন্য ফ্লোটিং পয়েন্ট লিটারেলস(Floating point literals) ব্যবহৃত হয়, যেমন: 2.5, 3.1416 etc
- ক্যারেক্টার লিটারেলস(Character Literals): ক্যারেক্টার(Character) ডাটা টাইপের জন্য ‘a’, ‘b’ ইত্যাদি ক্যারেক্টার লিটারেলস(Character literals) ব্যবহৃত হয়।
- স্ট্রিং লিটারেলস(String literals): স্ট্রিং(string) ডাটা টাইপের জন্য “Hello”, “World” ইত্যাদি স্ট্রিং লিটারেলস (String literals) ব্যবহৃত হয়।
- এস্কেপ সিকোয়েন্স লিটারেলস(Escape Sequence literals): ‘\n’, ‘\t’ ইত্যাদি এস্কেপ সিকোয়েন্স(Escape sequence) লিটারেলস(literals।
What is keyword in C ?
C programming এ Keyword : কিওয়ার্ড(Keyword) হলো C programming Language এর একটি রিজার্ভড ওয়ার্ড(reserved word) যার নির্দিষ্ট একটি অর্থ রয়েছে। কিওয়ার্ডগুলো(keywords) কোন আইডেন্টিফায়ার( Identifier) হিসেবে ব্যবহার করা যাবে না।
C programming এ মোট 32 টি কিওয়ার্ড(Keyword) রয়েছে:
| auto | double | int | struct |
| break | else | long | switch |
| case | enum | register | typedef |
| char | extern | return | union |
| const | float | short | unsigned |
| continue | for | signed | void |
| default | goto | sizeof | volatile |
| do | if | static | while |
এই কিওয়ার্ডগুলোকে(keywords) রিজার্ভ(Reserved) করে রাখা হয়েছে এবং কোন আইডেন্টিফায়ার (identifier) হিসেবে ব্যবহার করা যাবে না। এগুলো ছাড়াও আরো কিছু পূর্ব-সংজ্ঞায়িত (predefined) কিওয়ার্ড (keyword) রয়েছে যেমন printf, scanf ইত্যাদি।
What is the Basic structure of C programming?
| 1 | #include<stdio.h> | Header file |
| 2 | int main() | main function |
| 3 | { | starting block |
| 4 | printf(“Welcome to mhalder.com“); | statement |
| 5 | return 0; | return statement |
| 5 | } | end of the main block |
What is variable and their rules ?
Variable: ভেরিয়েবল হলো একটি ডাটা সংরক্ষণের জায়গার নাম যাতে প্রোগ্রামের প্রচালনার সময় ভ্যালু সংরক্ষণ করা যায়। উদাহরণস্বরূপ: int age; এখানে age হলো একটি ভেরিয়েবল যা int (ইন্টিজার) টাইপের।
ভেরিয়েবলগুলো প্রোগ্রামের প্রয়োজনে নির্দিষ্ট ডাটা টাইপ অনুসারে ডিক্লেয়ার করা হয়। প্রোগ্রাম পরিচালনার সময় এই ভেরিয়েবলগুলোতে ভ্যালু রাখা হয় এবং প্রয়োজনে সেগুলো পড়া যায় অথবা পরিবর্তন করা হয়।
Variable declaration এর নিয়ম:
- প্রতিটি ভেরিয়েবল এর নাম বর্ণমালা বা আন্ডারস্কোর (_) দিয়ে শুরু হওয়া উচিত।
- ভেরিয়েবল ঘোষণায় কোনো space allow করা যাবে না।
- আন্ডারস্কোর (_) ব্যতীত মাঝখানে অন্য কোন বিশেষ চিহ্ন ব্যবহার করা যাবে না ।
- কোন কীওয়ার্ড কে ভেরিয়েবল নাম হিসাবে ব্যবহার করা যাবে না।
- ভেরিয়েবলের সর্বোচ্চ দৈর্ঘ্য 8 অক্ষর কম্পাইলার এবং অপারেটিং সিস্টেমের উপর নির্ভর করে।
what is Gloal variable and local Variable in C programming?
Global Variable: গ্লোবাল ভেরিয়েবলগুলি সমস্ত ফাংশনের বাইরে সংজ্ঞায়িত করা হয়, সাধারণত প্রোগ্রামের উপরে। গ্লোবাল ভেরিয়েবলগুলি আপনার Programme এর life-time মান ধরে রাখতে পারে ।
Local Variable: একটি লোকাল ভেরিয়েবল একটি ফাংশন বা একটি ব্লকের ভিতরে ঘোষণা করা হয়। লোকাল ভেরিয়েবল এর মান ঐ ফাংশান বা ব্লকের মধ্যে সীমাবদ্ধ।
//Example of Global and Local variable
#include<stdio.h>
#include<conio.h>
int x; // global variable
void main()
{
int y; // local variable
x=11, y=22;
printf("Value of x : %d",x);
printf("Value of y : %d",y);
getch();
}what is Operator and how to use in C programming ?
অপারেটর (Operator) হলো এমন একটি চিহ্ন যা এক বা একাধিক অপারেন্ডকে নিয়ে কোন অপারেশন সম্পাদন করে এবং ফলাফল রিটার্ন করে। Operator Category-র লিস্ট নিচে দেওয়া হল ।
| Category | Operator |
| Arithmetic Operators | +, -, *, /, % |
| Relational Operators | ==, !=, >, <, >=, <= |
| Logical Operators | &&, ||, ! |
| Bitwise Operators | &, |, ^, ~, <<, >> |
| Assignment Operators | =, +=, -=, *=, /=, %=, &=, ^=, |=, <<=, >>= |
| Increment and Decrement Operators | |
| Conditional Operators | |
| Comma Operator |
what is operator precedence and associativity in C programming ?
Precedence: অপারেটর প্রাধান্য হলো অপারেটরগুলোকে একটি নির্দিষ্ট ক্রমে বা প্রাধান্য অনুযায়ী ব্যবহার করা। একটি এক্সপ্রেশনে একাধিক অপারেটর থাকলে প্রাধান্য অনুসারে অপারেটরগুলো কাজ করবে।
Associativity: প্রোগ্রাম এক্সপ্রেশনে যদি একই Precedence এর একাধিক অপারেটর থাকে তখন এক্সপ্রেশন বামদিক থেকে ডান দিকে অথবা ডানদিক থেকে বামদিকে অপারেটরগুলির কার্য সম্পন্ন হয় যে বৈশিষ্ঠ্যের দ্বারা ,তাকে অপারেটর অ্যাসোসিয়েটিভিটি (Associativity) বলে ।
| Precedence | Associativity | Operator Category | operators |
| Highest | Left to Right | Parentheses | () [] |
| Right to Left | Unary plus Unary Minus increment Decrement Logical Negation One’s Complement Pointer reference(Indirection) Address Size of type cast | + – ++ — ! ~ * & sizeof (type) | |
| Left to Right | Multiplicative Division Modulus | * / % | |
| Left to Right | Addition Substraction | + – | |
| Left to Right | Bitwise Left Shift Bitwise Right Shift | << >> | |
| Left to Right | Relational | <, <=, >, >= | |
| Left to Right | Equality Inequality | == != | |
| Left to Right | Bitwise AND | & | |
| Left to Right | Bitwise XOR | ^ | |
| Left to Right | Bitwise OR | | | |
| Left to Right | Logical AND | && | |
| Left to Right | Logical OR | || | |
| Right to Left | Conditional | ?: | |
| Right to Left | Assignment | = += -= *= /= %= &= ^= |= <<= >>= | |
| Left to right | Comma | , | |
| Lowest |
Increment/decrement operator in C programming with example?
Increment/Decrement Operator হল unary operator যা Operand Value এর মান 1 বৃদ্ধি / হ্রাস করতে ব্যবহৃত হয়। Increment Operator ডবল প্লাস চিহ্ন (++) এবং Decrement Operator ডবল মাইনাস চিহ্ন (–) দ্বারা চিহ্নিত করা হয়। ইহা দুই প্রকার, Pre-Increment/decrement এবং Post-Increment/decrement Operator
Pre-increment / Decrement Operator:
Pre-increment/decrement Operator টি এক্সপ্রেশনে বরাদ্দ (assigning to expression) করার আগে Operand এর মূল মান 1 দ্বারা বৃদ্ধি / হ্রাস করতে ব্যবহৃত হয়। Syntax: a=++m / –m;
Example: ধরা যাক m=2, a=++m /–m এই expression এ m এর মান a তে বরাদ্দ হওয়ার আগেই m এর মান 1 বৃদ্ধি / হ্রাস পায় অর্থাৎ a=3 এবং m=3 হয় / a=1 এবং m=1।
Post-increment/Decrement Operator:
Post-increment /Decrement Operator টি এক্সপ্রেশনে বরাদ্দ (assigning to expression) করার পরে Operand এর মূল মান 1 দ্বারা বৃদ্ধি / হ্রাস পায়। Syntax: a=m++/m– ;
Example: ধরা যাক m=2, a=m++ / m– এই expression এ m এর মান a তে বরাদ্দ হওয়ার পরেই m এর মান 1 বৃদ্ধি / হ্রাস পায় অর্থাৎ a=2 এবং m=3 হয় / a=2 এবং m=1 ।
What is Type Casting with Example?
Type Casting : একটি ডেটাটাইপকে অন্য একটি ডেটাটাইপ এ রূপান্তর করাকে টাইপ কাস্টিং(Type Casting ) বা টাইপ-রূপান্তর( Type Changing) বলা হয় । আপনি নিম্নরূপ কাস্ট অপারেটর(Cast Operator) ব্যবহার করে স্পষ্টভাবে এক প্রকার থেকে অন্য প্রকারে মানগুলিকে রূপান্তর করতে পারেন – (type_name) expression
//Example
main() {
int sum = 26, div = 5;
double result;
Result = (double) sum / div;
printf("Result is : %f\n", Result );
}What is Decision Making Statement ?
Mention Type of Decision Making statement with example?
Decision making Statement: Decision making Statement প্রোগ্রামের দিক এবং প্রবাহ নির্ধারণ করে। এগুলি conditional statement name পরিচিত কারণ তারা একটি সত্য বা মিথ্যা বুলিয়ান মান মূল্যায়ন করা বুলিয়ান এক্সপ্রেশন সহ শর্তগুলি নির্দিষ্ট করে।শর্ত সত্য হলে, কোডের একটি প্রদত্ত ব্লক কার্যকর হবে; শর্ত মিথ্যা হলে, ব্লক কার্যকর হবে না।
C/C++-এ সিদ্ধান্ত নেওয়া নিম্নলিখিত বিবৃতি দ্বারা করা যেতে পারে।
- If statement
- If..else statement
- if..else-if statement
- Nested if statement
- Switch statement
- Jump statement
- break
- continue
- goto
- return
What is switch case /Menu driven program ?
C programming language এ switch case হল if-else-if ladder statement এর বিকল্প হিসাবে ব্যবহার করা হয়,যা অনেকগুলি operation কে বিভিন্ন মানের ভিত্তিতে একসাথে execute করতে ব্যবহার করা হয়। “switch” and “case” keyword ব্যবহার করে switch case টিকে রূপ দেওয়া হয়। প্রত্যেকটি “case” এর শেষে break keyword ব্যবহার করা হয়ে থাকে। switch এর প্রত্যেক case প্রমানিত হলে default statement টি execute হয়।
Syntax: switch(expression){
case value1: ..statement 1;
break;
case value2: statement 2;
break;
case value3: statement 3;
break;
default: statement true if case1,case2,case3 are are false;
}What is Looping statement in C programming
Type of Looping Statement
Difference between various Looping statement
Loop: একটি লুপ স্টেটমেন্ট আমাদের একটি statement বা statement group কে একাধিকবার কার্যকর করতে ব্যবহৃত হয়। বেশিরভাগ প্রোগ্রামিং ভাষায় লুপ স্টেটমেন্টের সাধারণ রূপ নিচে দেওয়া হল।
C programming language এ সাধারণত তিন ধরনের লুপিং স্টেটমেন্ট ব্যবহার করা হয় –
For Loop : Statement গুলির একটি Sequence একাধিকবার কার্যকর করে এবং কোডটি সংক্ষিপ্ত করে যা লুপ ভেরিয়েবল পরিচালনা করে।
Syntax: for(initilization; condition; incremnet/decrement);
example: for(int x=0; x<10; x++)
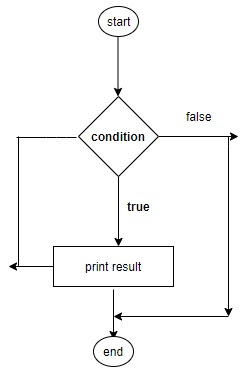
While Loop : প্রদত্ত শর্ত সত্য থাকাকালীন একটি বিবৃতি বা বিবৃতির গ্রুপ পুনরাবৃত্তি করে। এটি লুপ বডি কার্যকর করার আগে শর্তটি পরীক্ষা করে।
Syntax: while(condition){
statement;
increment/decrement;
}
example:
while(x<10){
printf("Vale of x=%d",x);
x++
}
Do..While Loop: এটি অনেকটা while loop এর মতো, এটি লুপ বডি কার্যকর করার পরে শর্তটি পরীক্ষা করে।
Syntax: do{
printf("Message");
increment/decrement;
} while(condition);
example: do{
printf("Vale of x=%d",x);
x++
} while(x<10);nested Loop: একটি for, while ,do..while loop এর ভিতরে যখন এক বা একাধিক ঐ for, while ,do..while loop ব্যবহার করা তখন সেটি nested Loop নামে পরিচিত হয় ।
Loop Control Statement :
লুপ কন্ট্রোল স্টেটমেন্ট তার স্বাভাবিক sequence থেকে Execution এ পরিবর্তন করে। যখন Execution একটি সুযোগ ছেড়ে যায়, সেই সুযোগে তৈরি করা সমস্ত স্বয়ংক্রিয় বস্তু ধ্বংস হয়ে যায়।
Control Statement গুলি হল –
- Break statement
- Control Statement
- goto statement
যে কোন প্রোগ্রামিং ল্যাঙ্গুয়েজ এ আর ও একটি লুপ এর ব্যবহার অনেক দেখা যায় সেটি হল infinite loop .
// 1
while(1)
{
//statement
}
// 2
for(; ;) { ...}Call by Value এবং Call by Reference এর পার্থক্য লেখ
| Call by Value | Call by Reference |
| Original Value এর কোনো পরিবর্তন হয় না। | এখানে Original Value এর পরিবর্তন হয় । |
| এখানে ভেরিয়েবলের অনুলিপি (Copy of variable) পাস হয়ে থাকে। | এখানে ভেরিয়েবল নিজেই পাস হয়ে থাকে। |
| Actual এবং Formal Argument ভিন্ন ভিন্ন Memory Location এ তৈরি হয় | Actual এবং Formal Argument একই Memory Location এ তৈরি হয়। |
| Actual এবং Formal Argument একই Memory Location এ তৈরি হয়। | ভেরিয়েবলের ঠিকানা (Address of Variable)সঞ্চয় করতে পয়েন্টার এর প্রয়োজন হয় । |
| int main() { int x = 10; printf(“before calling=%d”,x); increment(x); printf(“After calling=%d”,x); getch(); } void increment(int a) { a = a + 1; printf(“value is=%d”,a); } | int main() { int x = 10; printf(“before calling=%d”,x); increment(&x); printf(“After calling=%d”,x); getch(); } void increment(int *a) { *a = *a + 1; printf(“value is=%d”,*a); } |
Dynamic Memory Allocation
অ্যারে(Array) হ’ল একটি নির্দিষ্ট সংখ্যক মানের সংগ্রহকরন । একবার অ্যারের আকার ঘোষণা (Array Size Declaration) হয়ে গেলে আপনি এটিকে পরিবর্তন করতে পারবেন না।
কখনও কখনও আপনি ঘোষিত অ্যারের আকার(Array Size) অপর্যাপ্ত হতে পারে। এই সমস্যাটি সমাধান করার জন্য, Run Time -এ আপনি mannualy memory allocation করতে পারেন। এটি প্রোগ্রামিংয়ে (Programming) Dynamic Memory Allocation নামে পরিচিত।
Dynamic Memory Allocation- এর জন্য C Programming Language কতগুলি Library Function ব্যবহার করা হয় এবং এগুলি “stdlib.h” নামক header file -এ defined করা থাকে। Library Function গুলি হল-
- malloc()
- calloc()
- realloc()
- free
malloc() কি? উদাহারন সহযোগে ব্যাখ্যা কর ।
malloc() function-এর অর্থ হল- memory allocation- যা নির্দিষ্ট সংখ্যক বাইটের মেমরির একটি ব্লক(Single block of memory) সংরক্ষণ করে।এটি void pointer return করে যার ফলে যে কোনও form-এর pointer-এ cast করা যায়। malloc() function ব্যবহার করলে মেমরি uninitialized অবস্থায় থাকে।
Syntax: ptr= (castType*)malloc(size);
Example: ptr = (int*) malloc(10 * sizeof(int));
উপরিউক্ত উদাহারন থেকে বলতে পারি 10*4=40 byte size এর মেমরির একটি ব্লক বরাদ্দ (allocate) হয়েছে। এখানে বরাদ্দকৃত মেমরির প্রথম বাইট (First byte of allocated memory) -এর address কে point করে ptr .
Example :
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
// Allocate memory for an array of 5 integers
int *arr = (int *)malloc(5 * sizeof(int));
// Check if memory allocation was successful
if (arr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed. Exiting the program.\n");
return 1;
}
// Initialize the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
arr[i] = i * 2;
}
// Display the array elements
printf("Array elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// Free the dynamically allocated memory
free(arr);
return 0;
}
calloc() কি? উদাহারন সহযোগে ব্যাখ্যা কর ।
calloc() function-এর অর্থ হল- contiguous allocation- যা নির্দিষ্ট সংখ্যক বাইটের মেমরির অনেকগুলি ব্লক(multiple block of memory) সংরক্ষণ করে। calloc() function ব্যবহার করলে মেমরি প্রত্যেক টি বিট-এর মান শূন্য হয়ে যায়।
Syntax: ptr= (castType*)calloc(n,size);
Example: ptr = (int*) calloc(5 ,sizeof(int));
উপরিউক্ত উদাহারন থেকে বলতে পারি মেমরিতে 5 ব্লক বরাদ্দ (allocate) হয়েছে যার প্রত্যেক টির আকার 5*4=20 byte ।
Example
int main() {
// Allocate memory for an array of 5 integers using calloc
int *arr = (int *)calloc(5, sizeof(int));
// Check if memory allocation was successful
if (arr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed. Exiting the program.\n");
return 1;
}
// Display the array elements (initialized to 0 by calloc)
printf("Array elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// Free the dynamically allocated memory
free(arr);
return 0;}
realloc() কি? উদাহারন সহযোগে ব্যাখ্যা কর ।
realloc()- re- allocation অর্থাৎ malloc()/ calloc() দ্বারা পূর্বে বরাদ্দকৃত মেমরির পুনরায় বৃদ্ধি অথবা হ্রাস করা।
Syntax: ptr= realloc(ptr,size);
Example
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
// Allocate memory for an array of 3 integers
int *arr = (int *)malloc(3 * sizeof(int));
// Check if memory allocation was successful
if (arr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory allocation failed. Exiting the program.\n");
return 1;
}
// Initialize the array elements
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
arr[i] = i * 2;
}
// Display the original array elements
printf("Original array elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; ++i) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// Resize the array to hold 5 integers using realloc
arr = (int *)realloc(arr, 5 * sizeof(int));
// Check if reallocation was successful
if (arr == NULL) {
fprintf(stderr, "Memory reallocation failed. Exiting the program.\n");
return 1;
}
// Initialize the additional elements
for (int i = 3; i < 5; ++i) {
arr[i] = i * 2;
}
// Display the updated array elements
printf("\nUpdated array elements: ");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
printf("%d ", arr[i]);
}
// Free the dynamically allocated memory
free(arr);
return 0;
}
free() কি? উদাহারন সহযোগে ব্যাখ্যা কর ।
free() -এই function টি ব্যবহার করলে malloc()/calloc() দ্বারা বরাদ্দকৃত মেমরি মুক্ত হয়।
Syntax: free(ptr);
উপরের উদাহারন গুলি তে উল্লেখ করা হয়েছে free() এর ব্যবহার ।
File in C programming
C Programming language-এর নিম্নলিখিত term গুলি উদাহারন সহ ব্যাখ্যা কর । 1)fseek() 2)fwrite()
fseek(): fseek ফাংশনটি ফাইলের অবস্থান নির্দেশককে একটি ফাইলের একটি নির্দিষ্ট স্থানে সরাতে ব্যবহৃত হয়।
Syntax: FILE *FilePointer
fseek(FilePointer,OffsetValue, StartPosition)
FilePointer হল একটি ফাইল অবজেক্টের একটি পয়েন্টার যা আগে fopen() ব্যবহার করে খোলা হয়েছিল।
OffsetValue হল ফাইলের অবস্থান নির্দেশক সরানোর জন্য বাইটের সংখ্যা।
StartingPosition হল-যেখানে অফসেট প্রয়োগ করা হয় সেখান থেকে অবস্থান।
এটি নিম্নলিখিত মানগুলির মধ্যে একটি নিতে পারে:
SEEK_SET: অফসেট ফাইলের মান প্রথম থেকে শুরু হবে (0)।
SEEK_CUR: অফসেটটি ফাইলের মান বর্তমান অবস্থান থেকে শুরু হবে(2)।
SEEK_END: অফসেট ফাইলের মান শেষ থেকে শুরু হবে (1)।
fwrtie(): fwrite ফাংশনটি একটি ফাইলে ডেটা লিখতে ব্যবহৃত হয়। fwrite ফাংশনের জন্য Syntax হল:
size_t fwrite(const void *ptr, size_t size, size_t count, FILE *stream);
‘ptr’- ডাটা লেখার জন্য একটি পয়েন্টার ব্যবহার হয়।
‘size’- Size হল বাইটে প্রতিটি উপাদানের আকার(Size)।
‘count’-File এর মধ্যে যত গুলি element কে লিখতে হবে তার সংখ্যা বোঝায়
‘stream’-স্ট্রিম হল একটি ফাইল অবজেক্টের(File Object)একটি পয়েন্টার(pointer)যা আগে fopen() ব্যবহার করে খোলা হয়েছিল
example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
FILE *fp;
char str[] = "This is a test";
fp = fopen("file.txt", "w+");
if(fp == NULL) {
perror("Error opening file");
return -1;
}
fseek(fp, 5, SEEK_SET);
fwrite(str, sizeof(char), sizeof(str), fp);
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}Command Line argument বলতে কি বোঝ? এটির Syntax-টি লেখ ।
প্রোগ্রামিংয়ে কমান্ড লাইন আর্গুমেন্ট(Command Line argument) একটি গুরুত্বপূর্ণ ধারণা। main() এর মধ্যে argument/parameter প্রেরন করা হয় এবং বাইরে থেকে অর্থাৎ Command Line থেকে নিয়ন্ত্রন করার চেষ্টা করা হয়
Syntax:int main(int argc, char *argv[])
এখানে main() – এর মধ্যে দুটি parameter/argument প্রেরন করা হয়েছে। “argc”– কমান্ড লাইন (Command Line)- এর মধ্যে parameter/argument-এর সংখ্যা গণনা করে “argv[]”– একটি পয়েন্টার অ্যারে যা char type পয়েন্টার ধারণ করে প্রোগ্রামে পাস হওয়া parameter/argument কে নির্দেশ করে।
List of some important C programming using loop
Write a program to find the largest number between two number
#include<stdio.h>
int main()
{
int a=6,b=8;
if(a>b)
printf("a is the large number=%d ",a);
else
printf("b is the large number=%d ",b);
}Write a program to find the largest number among three number
1) using nested if else 2) using ternary operator
//1. using nested if else
int main()
{
int a=6,b=8,c=10;
if(a>b)
if(a>c)
printf("a is large =%d ",a);
else
printf("c is large =%d ",c);
else
if(b>c)
printf("b is large =%d ",b);
else
printf("c is large =%d ",c);
return 0;
}
//2. using Ternary conditional Operator
int main()
{
int a=6,b=8,c=10, result;
result=(a>b) ? (a>c) ? a:c :(b>c)? b:c ;
printf("")
return 0;
}Write a program to find the largest number among Four number
1) using nested if else 2) using ternary operator
// 1) using nested if else
int main()
{
int a=6,b=8,c=10,d=7;
if(a>b)
if(a>c)
if(a>d)
printf("a is large =%d ",a);
else
printf("d is large =%d ",d);
else
if(b>c)
if(b>d)
printf("b is large =%d ",b);
else
printf("d is large =%d ",d);
else
if(c>d)
printf("c is large =%d ",c);
else
printf("d is large =%d ",d);
return 0;
}
// 2) using Ternary conditional Operator
int main()
{
int a=6,b=8,c=10, result;
result=(a>b) ? (a>c) ? a:c :(a>d)? b:c : (b>c) ? (b>d) ? b:d : (c>d) ? c:d ;
//result=( (a>b && a>c && a>d) ? a : (b>c && b>d) ? b : (c>d)? c : d );
printf("Large Number is=%d",result);
return 0;
}WAP in C to calculate Sum of 1st n natural number
#include <stdio.h>
int main()
{
int n, i, sum = 0; // initialize and declare the local variables
printf("Enter a positive number : ");
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i=0; i<=n; i++){
sum=sum+i;
}
printf(" \n Sum of first %d natural number is : %d", n, sum);
getch();
return 0;
}WAP in C to Check whether given number is prime or not
#include <stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main() {
int n, i, status = 0;
printf("Enter a positive integer: ");
scanf("%d", &n);
// 0 and 1 are not prime numbers
if (n == 0 || n == 1)
status = 1;
for (i = 2; i <=sqrt(n); ++i) {
// can write for(i=2; i<=n or i<=n/2; i++)
if (n % i == 0) {
// change status to 1 for non-prime number
status = 1;
break;
}
}
if (status == 0)
printf("%d is a prime number.", n);
else
printf("%d is not a prime number.", n);
getch();
return 0;
}WAP in C to display all the prime number between 1 to 100
#include<stdio.h>
#include<math.h>
int main() {
int l, u, i, status; // l=lower and u=upper
printf("Enter two numbers(intervals): ");
scanf("%d %d", &l, &u);
printf("Prime numbers between %d and %d are: ", l, u);
// iteration until low is not equal to high
while (l < u) {
status = 0;
// ignore numbers less than 2
if (l<= 1) {
++l;
continue;
}
// if low is a non-prime number, status will be 1
for (i = 2; i <=sqrt(l); ++i) {
// can write i=2; i<l/2; i++)
if (l % i == 0) {
status = 1;
break;
}
}
if (status == 0)
printf("%d ", l);
// increase lower by 1 to check prime for the next number
++l;
}
getch();
return 0;
}WAP in c to check given number is perfect number or not.
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int num,i=1,sum=0;
printf("Enter positive number: ");
scanf("%d",&num);
while(i<num){
if(num%i==0)
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}
if(sum==num)
printf("%d is a perfect number",i);
else
printf("%d is not a perfect number",i);
getch();
return 0;
}WAP in C to print perfect numbers from 1 to 100
#include<stdio.h>
int main(){
int num,i,sum;
printf("Perfect numbers are: ");
for(num=1;num<=100;num++){
i=1;
sum = 0;
while(i<num){
if(num%i==0)
sum=sum+i;
i++;
}
if(sum==num)
printf("%d ",num);
}
getch();
return 0;
}